|
|
 |
|

|
Analog and Digital Behavioral Modeling
|

|
|
| |
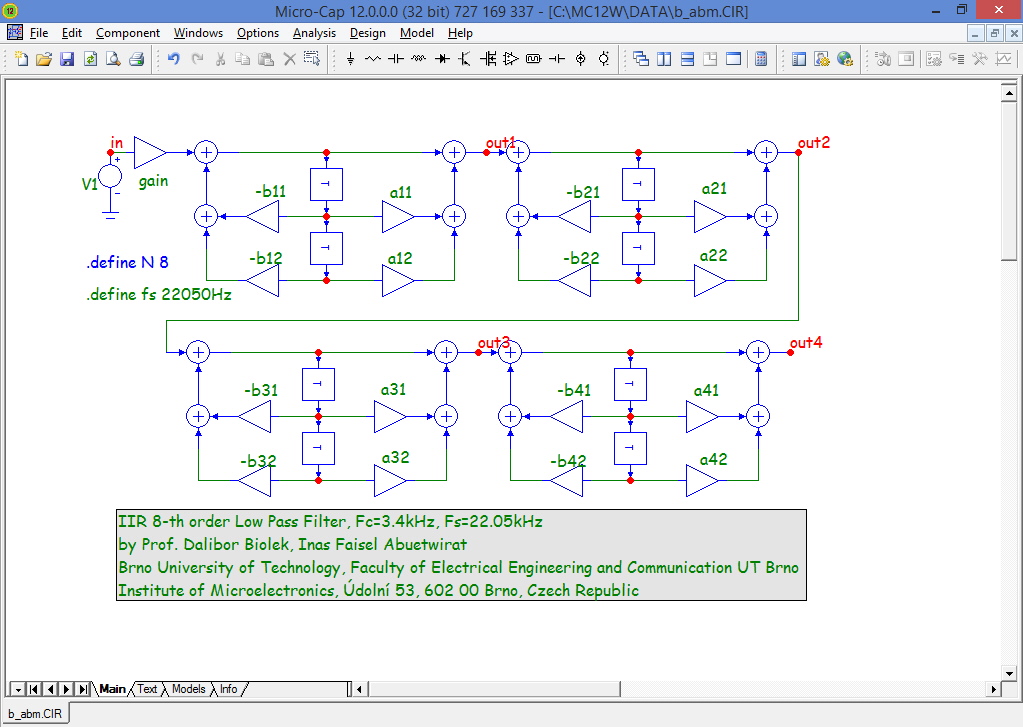
Laplace sources let you describe the S-plane linear transfer function
of a circuit block. Function sources let you model nonlinear behavior.
The source can be a mathematical function of any other circuit variable,
such as a node voltage or a device current. Z transform sources let you
handle Z transform expressions as, for example, in digital filters.
Expressions can also be used for resistor, capacitor, and inductor
values. Here are some samples:
G*b0/(s**2+b1*s+b0): low pass filter
exp(-c*s*(r+s*l)**.5): transmission line
-k*(v(p)-v(c)+u*(v(g)-v(c)))**1.5: a triode
VZ+tempco*(TEMP-27): reference voltage source
Sin(2*pi*T)*Exp(-T): damped sine wave source
Powerful digital behavioral primitives include logic expressions,
pin delay blocks, and constraint checkers. These allow modeling of
complex commercial parts like adders, multipliers, converters, and
arithmetic logic units.
|
| |
|
|
|



