|
|
 |
Stability Analysis
Stability analysis uses either the Middlebrook or Tian method to calculate the closed
loop Gain Margin and Phase Margin. To use this method the user chooses a place
in the circuit to insert a probe. The program breaks the loop at this probe point and
measures the appropriate parameters needed in the calculation. To demonstrate the
use of Stability Analysis we'll use the file, STABILITY.CIR. It looks like this:
|
In this feedback amplifier we want to find the gain and phase margins. Press Alt+0 to
select Stability Analysis. Press F2 to start the run and you'll see this:
|
|
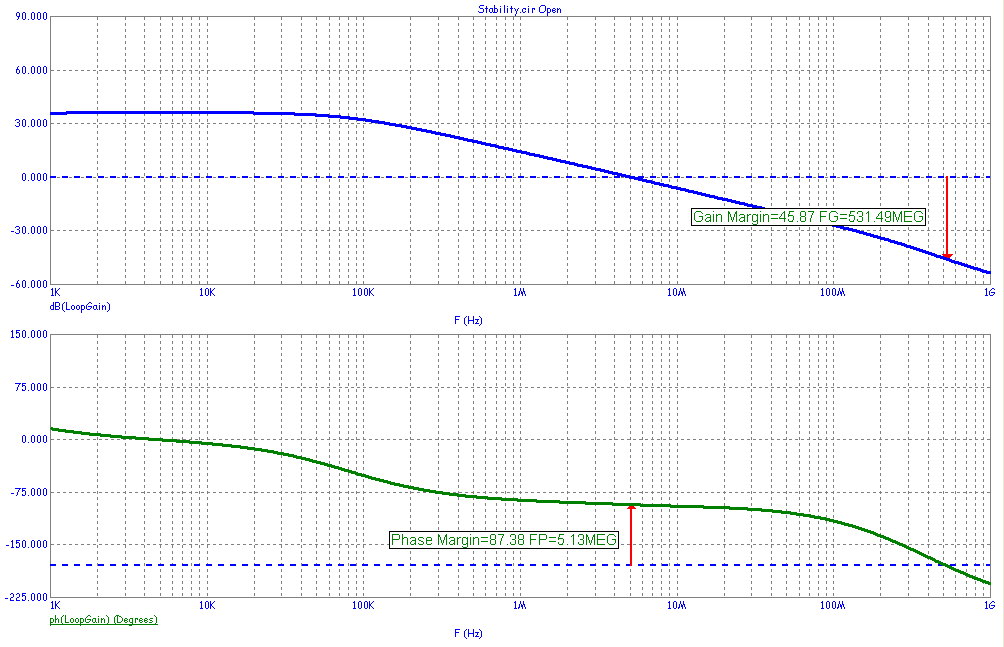
The Gain Margin is measured at 45.87 dB and the Phase Margin at 87.38 degrees.
How does it work? The user inserts the probe component at any point in the loop. At
the point of this probe, MC11 replaces the probe component with suitable voltage
and current sources to measure closed loop voltage and current gains. During the run
the variable Loop is stepped from 1 to 2 and the sources Vinj and Iinj take on these
AC values:
if Loop==1 iol = 0 vol = 1
if Loop==2 iol = 1 vol = 0
The Tian method uses the following equation to determine the margins:
LoopGain = -1/(1-1/(2*(I(Vinj)@1*V(ol)@2-V(ol)@1*I(Vinj)@2)+V(ol)@1+I(Vinj)@2))
The equation in the LoopGain variable was derived from the Tian article. It uses the
step selection operator @ to combine the waveform results from different steps. For
example:
V(ol)@2 specifies the voltage at node ol during the second step of the simulation.
I(Vinj)@1 specifies the current through the source Vinj during the first step.
Together, the quantities V(ol)@1, V(ol)@2, and I(Vinj)@1 determine the variable LoopGain
and its plot is examined to determine the gain and phase margins.
The gain margin is computed as follows:
Gain Margin = -dB(LoopGain) where Phase(LoopGain) equals -180.
The phase margin is computed as follows:
Phase Margin = 180+Phase(LoopGain) where dB(Loopgain) equals 0.
For those who would like to read more of the theory behind these methods, we recommend
these references:
1) Tian Method:
"Striving for Small-Signal Stability", Michael Tian, V. Visvanathan, Jeffrey Hantgan,
and Kenneth Kundert, Circuits & Devices, January 2001.
2) Middlebrook Method:
"Measurement of Loop Gain in Feedback Systems", David Middlebrook, International
Journal of Electronics (volume 38, no. 4, pages 485-512, April 1975).
|
|
|
|
|






