|
|
 |
Two Models for Relays
Occasionally a relay model is needed. Here are two models that work well. The first model, called RELAY1, is a simple model that includes coil series resistance and inductance, and turn-on and turn-off currents. The other is a more sophisticated but slower running electromechanical model of the relay that includes such effects as coil resistance and inductance, turn-on and turnoff delays, nonlinear fringing inductance, plunger rebound and the associated switch bounce.
Here is the RELAY1 model:
To simplify the process, consider the following test circuit.
|
The input circuit of this model includes a user-specified coil resistance and inductance. The coil current is sensed and converted to a voltage by H1 which drives a Schmitt macro to provide hysteresis between the ION and IHOLD currents. The output of the Schmitt drives a standard voltage controlled switch S1.
The figure below shows the test circuit used.
|
The figure below shows the transient analysis limits.
|
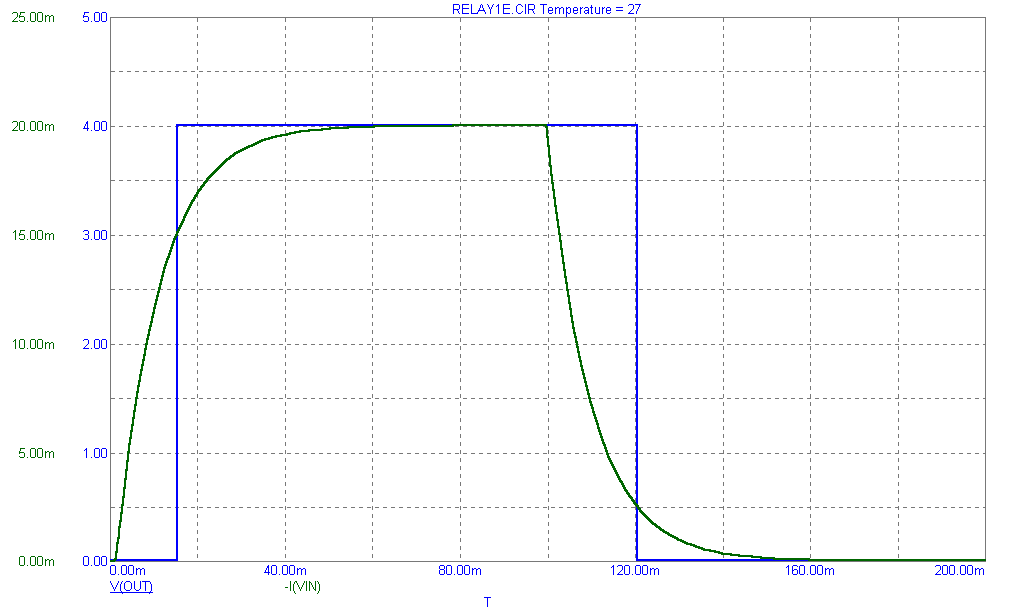
The transient analysis below shows the input current waveform and the voltage at the output switch. The switch changes closes at the specified current of 15mA and stays closed until the input current goes below the specified 2.5mA holding current.
|
|
The parameters for the RELAY1 model are as follows:
RCOIL
Resistance of the relay coil
LCOIL
Inductance of the relay coil
RON
Closed resistance of the output switch
ROFF
Open resistance of the output switch
ION
Input current required to close the relay contacts
IOFF
Input current required to hold the relay contacts closed
An electromechanical relay model
RELAY2 is a more complicated model. It includes a flux circuit and derives a magnetizing force from the flux. It then algebraically sums the magnetizing, stop, friction and restoring spring forces acting on the relay plunger to arrive at a net force which is integrated once to get the plunger velocity and again to get the plunger position. This plunger position directly controls the switch contacts.
Here is the model for the RELAY2 model:
|
The figure below shows the test circuit used.
|
The figure below shows the transient analysis limits..
|
The transient analysis above shows the input current waveform and the voltage at the output switch. The plot also shows the internal waveforms for the net force, plunger velocity, and plunger position.
The parameters for the macro are shown below. Other constants are defined within the macro and may be modified to produce different mechanical models.
Parameters
RCOIL
Resistance of the relay coil
LCOIL
Inductance of the relay coil
RON
Closed resistance of the output switch
ROFF
Open resistance of the output switch
Constants
AREA
Plunger area in square mm
M
Plunger mass in kilograms
KSPRING
Spring constant
KSTOP
Stopping force constant
KFORCE
Net force scaling constant
|
|
|
|
|






